This surge in technology isn’t merely about making things faster or cheaper. It’s about crafting a future where sustainability and efficiency go hand in hand. It’s about sparking innovation, enhancing productivity, and driving global economic growth. So, buckle up as we delve into the exciting realm of new manufacturing technology, where possibilities are as limitless as our collective imagination.
New Manufacturing Technology
This section focuses on what exactly constitutes new manufacturing technology.
Defining New Manufacturing Technology

New manufacturing technology, aka advanced manufacturing technology, represents a collection of modern methods and machinery aimed at enhancing industrial efficiency and productivity. This form of technology leverages the power of digitalization, automation, and advanced materials, transforming how products get designed, manufactured, and distributed.
A more succinct definition could be, new manufacturing technology is a broad area comprising different innovative technologies and processes that enhance manufacturing operations, enabling faster, efficient, and more sustainable production. Crucially, these technologies support better resource utilization, leading to cost efficiencies and reduction in environmental impact, supporting sustainable development goals.
Key Trends in New Manufacturing Technology
Automation and Robotics
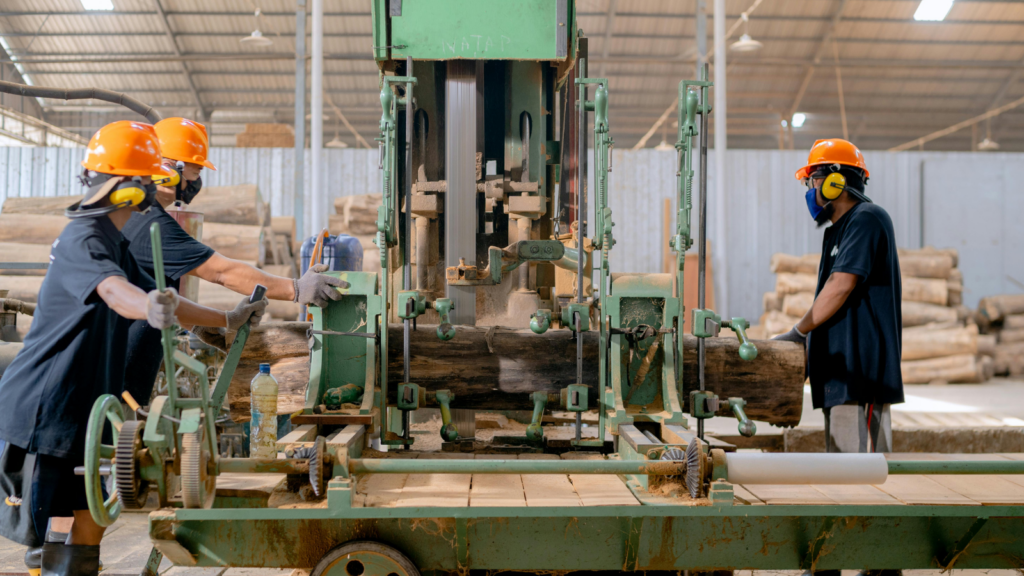
In the sphere of new manufacturing technology, automation and robotics rank at the forefront. Industrial robots, a prominent contributor to automation, eliminate human error while augmenting productivity. With automation, industries achieve improved control over complex tasks, thereby enhancing both production quality and volume.
Additive Manufacturing

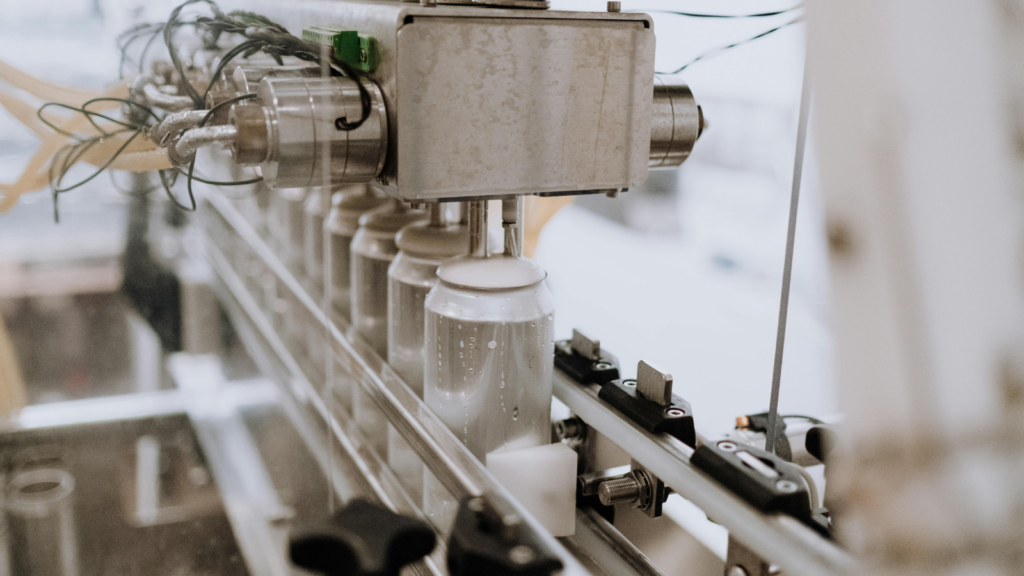
Additive Manufacturing, or 3D Printing, constructs three-dimensional objects from a digital design. This technology permits rapid prototyping that can drastically reduce the time from concept to creation. Take Stratasys, an industry leader in 3D printing, which offers solutions by designing and producing parts using computer-aided design (CAD) software. Aided by 3D printed parts, companies minimize storage costs, and achieve greater design freedom.
Sustainable Manufacturing Practices
“Going green” extends beyond just a social responsibility. For manufacturers, sustainable practices offer tangible benefits such as reduced emissions and waste, thereby lowering the environmental footprint. But it isn’t just about the environment, sustainability can also trim costs and enhance productivity. Hardddd evidence proves that by adopting eco-friendly practices, industries can effectively contribute to the global economic growth and sustainable development goals. By many accounts, the future of manufacturing shines green.
Challenges Facing the Implementation of New Technologies
Transitioning to new manufacturing technology, while holding tremendous promise, faces certain stumbling blocks, standing in its path. This section delves deeper into the complexities associated with each.
Financial Barriers
Adapting to new manufacturing technology, arguably, comes with a hefty price tag. Monetary resources play a critical role in acquiring, installing, and maintaining new machine systems, including automation equipment and 3D Printers. To illustrate, a high-grade industrial robot by KUKA, costs up to $100,000, a substantial investment for SMEs. Additionally, in order to ensure synthesizing efficient and environmentally sustainable manufacturing practices, industries might face extensive expenditure. For instance, Siemens’ energy-efficiency programs, despite offering long-term cost reduction, necessitate significant upfront investment.
Skill Gaps and Education

Next, skill gaps prevalent in workforces pose a significant hurdle in the adoption of new technologies. As manufacturing shifts towards more sophisticated, tech-driven processes, a mismatch emerges between available skills and those demanded. Workers, traditionally trained in manual tasks, now need to operate complex systems such as automation controls, robotics, and additive manufacturing machinery. Yet, many lack the necessary education or training. For example, to operate a Stratasys 3D Printer proficiently, one typically requires technical knowledge and specialized training, presenting a challenging learning curve for many. Bridging these skill gaps, through effective educational programs, remains a vital, yet challenging task.
The Exciting Realm of New Manufacturing Technology
Embracing new manufacturing technology brings a wave of change to the industrial sector. It’s clear that the benefits – from boosted productivity to remarkable cost savings and environmental advantages – are hard to ignore. Yet, it’s not without its hurdles. High equipment costs and skill gaps present real challenges. Overcoming these barriers, particularly through targeted education and training, is key to unlocking the full potential of these technologies. It’s a future that’s not just possible, but inevitable. The journey might be challenging, but the rewards are worth it. Let’s gear up for a new era in manufacturing, where technology takes the lead.